1. Overview of CLUPAN¶
1.1. Cluster expansion method and thermodynamic calculations using CLUPAN¶
Evaluation of effective cluster interactions (ECI) using the cluster expansion (CE) method.
Calculation of energies for structures using ECI.
Monte Carlo simulations using ECI.
Free energy calculation based on thermodynamics integration combined with Monte Carlo simulations.
Iterative procedure to perform the CE.
See [CE1] to find the details of the procedure.
A Seko, Y Koyama and I Tanaka, Phys. Rev. B 80, 165122 (2009).
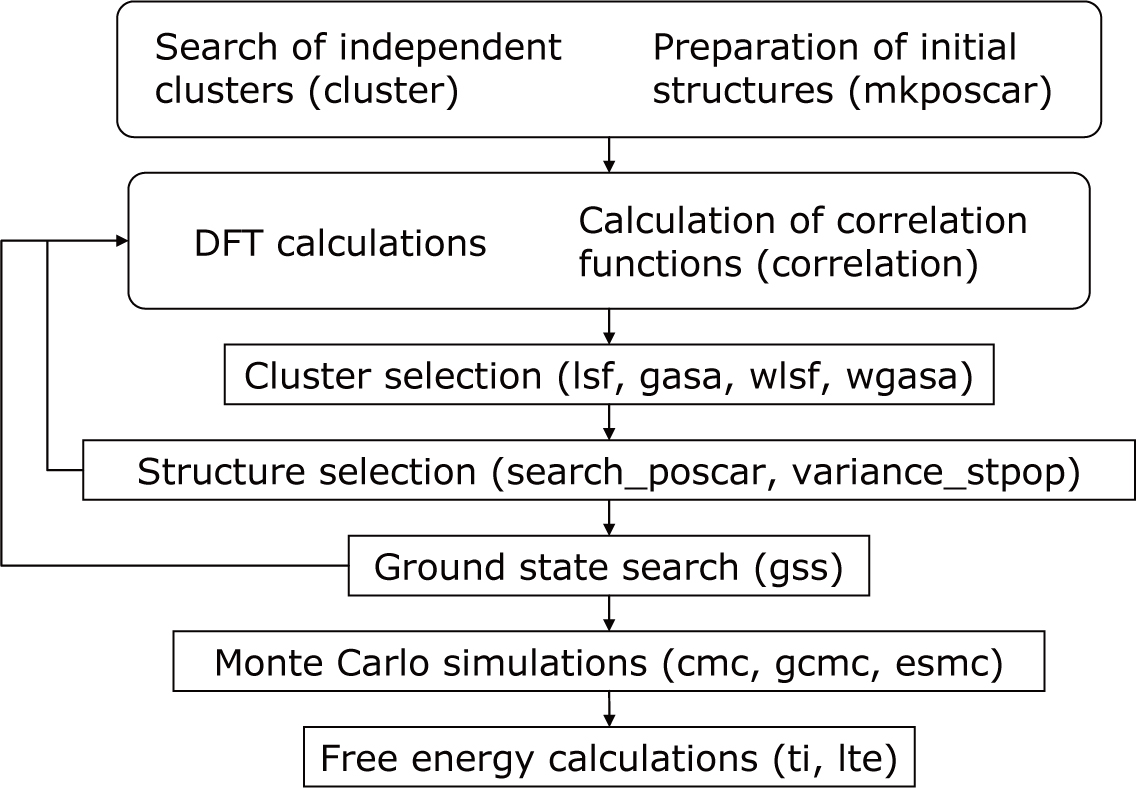
1.2. Framework of CLUPAN¶
CLUPAN is composed of the following programs.
main programs
- Searching for symmetrically-independent structures
mkposcar
- Searching for symmetrically-independent clusters
cluster
- Calculating correlation functions of a structure
correlation
- Estimating ECIs using the least-squares method
lsf, wlsf
- Optimizing cluster set using the genetic algorithm and the simulated annealing
gasa, wgasa
- Searching for DFT structures that improves the estimated ECIs
search_poscar
- Searching for ground state structures using the ECIs
gss
- Performing Monte Carlo simulations using the ECIs
cmc, gcmc
- estimating the grand potential using the thermodynamic integration
ti
sub programs
- Evaluating the variance of correlation functions and the correlation between correlation functions of two clusters
statistic
- Calculating the mean variance of the predicted energy
variance_energy
- Generating VARIANCE and MEAN files required in search_poscar_variance
variance_stpop
- Estimating the grand potential using the low temperature expansion
lte
1.3. Examples of calculations by using CLUPAN¶
Predicting cation disordering in spinel oxides [CE2]
Exploring stable structures in tin oxides [CE3]